How To Dye With Cutch (Acacia Catechu)
Share
How To Dye With Cutch (Acacia Catechu)
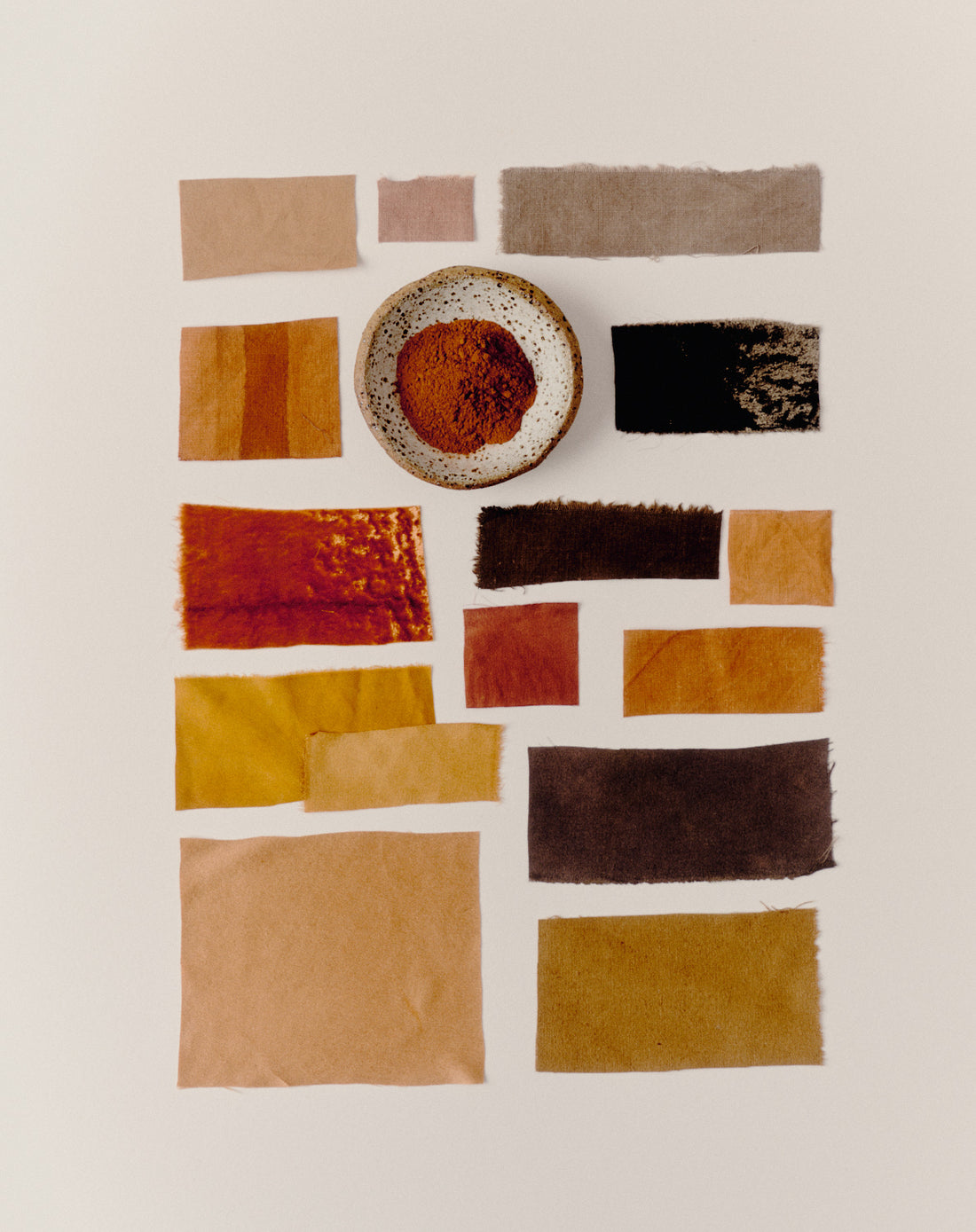
Cutch, derived from the wood of the Acacia catechu tree, is a remarkable natural dye that has been used for centuries in textile and craft industries. Known for its warm, earthy tones, cutch offers a sustainable alternative to synthetic dyes, making it a favourite among eco-conscious artisans and dyers. In this blog post, we’ll explore the origins, properties, and uses of cutch, as well as how to incorporate it into your dyeing projects.
What is Cutch?
Cutch is a natural dye obtained from the heartwood of the Acacia catechu tree, commonly found in regions of South and Southeast Asia, particularly in India. The dye is produced by extracting the tannins from the wood, resulting in a rich, brownish color that can vary in shade depending on the dyeing process and the mordant used.
Historical Significance
Historically, cutch has been an important dye in traditional Indian textiles, particularly in the production of fabrics such as khadi and indigo-dyed materials. Its use dates back to ancient times, and it played a vital role in the dyeing practices of various cultures. Cutch has also been used in other applications, such as leather tanning and medicine, highlighting its versatility.
Dye Properties
Color Range
Cutch typically produces warm brown hues, which can vary from light tan to deep chocolate, depending on several factors:
- Mordants: Using different mordants, such as alum or iron, can significantly alter the resulting colour. For instance, alum may yield lighter, more golden shades, while iron can produce darker, more muted tones.
- Fibre Type: The material being dyed (wool, cotton, silk) also influences the final colour. Natural fibres tend to absorb the dye better, resulting in more vibrant hues.
Light and Wash Fastness
Cutch is known for its good light and wash fastness, meaning that fabrics dyed with cutch maintain their color well over time. This property makes it an excellent choice for textiles intended for wear or frequent washing.
How to Use Cutch in Dyeing
Materials Needed
- Cutch extract powder: Available in our shop
- Natural fibre: Cotton, linen, bamboo, hemp, wool, silk.
- Mordants: Alum is commonly used, but iron can be explored for darker shades.
- Large Pot: For dyeing.
- Water: For the dye bath.
- Stirring Utensil: Wooden or plastic spoon.
Dyeing Process
- Prepare the Fibre: Scour/wash your fibre in hot water with some washing soda and gentle detergent. Then, pre-treat your fibre with a mordant. For alum, dissolve it in warm water and soak the fibre for an hour, then rinse.
- Make the Dye Bath: In a large pot, add the cutch extract with enough water for your fibre to move freely. The extract powder should dissolve fairly quickly.
- Dye the Fibre: Add the pre-treated fibre to the dye bath. Simmer for 30 minutes to an hour, stirring occasionally. For deeper colours, let the fibre soak longer, checking frequently to achieve your desired shade.
- Rinse and Dry: Once you’re satisfied with the colour, rinse the fibre in cool water until the water runs clear. Hang to dry in a shaded area.
Eco-Friendly
Cutch is a biodegradable, non-toxic dye, making it a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious creators. Using natural dyes like cutch reduces reliance on synthetic chemicals, benefiting both the environment and your health.